Changes (mutations) in the DNA sequence in BRCA1 or BRCA2 that prevent their corrective function are called harmful variants. Harmful variants increase the risk of certain cancers, most notably breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
As we have mentioned in recent articles, genetic factors are one of the important causes leading to breast cancer progression, in which the role of BRCA1,2 gene mutations is often mentioned. mention. According to statistics, about 3% of breast cancer cases (about 7,500 women each year) and 10% of ovarian cancer cases (about 2,000 women each year) are caused by genetic mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
.
WHAT ARE BRCA 1 AND BRCA 2?
BRCA1 and BRCA2 are genes that encode proteins that help repair damaged DNA, and help protect against some cancers. Everyone has two copies of the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene, one inherited from the mother and one from the father. Changes (mutations) in the DNA sequence in BRCA1 or BRCA2 that prevent their corrective function are called harmful variants. Harmful variants increase the risk of certain cancers, most notably breast cancer and ovarian cancer. A person carries changes inherited from a parent known as a genetic mutation. If one family member has had breast or ovarian cancer due to a mutation in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes, subsequent generations are likely to inherit the same type of mutation in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. BRCA2. Therefore, it is necessary to perform BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation screening tests for the remaining members.
.
.
HOW DO BRCA1 OR BRCA2 GENE MUTATIONS INCREASE THE RISK OF BREAST CANCER AND OVARIAN CANCER IN WOMEN?
A woman's risk of breast and/or ovarian cancer increases significantly if she inherits a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation, and her risk of developing cancer will be faster than in a group without the mutation. The increased risk for different types of cancer is different, depending on the type of mutation.
.
- Breast cancer: About 13% of women in general are at risk of breast cancer due to different causes. In particular, the incidence of breast cancer in women with BRCA1 mutations is 55-72% and 45-69% for women with BRCA2 mutations.
.
Like patients with breast cancer from other causes, those who have been diagnosed with unilateral breast cancer due to a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation also have an increased risk of developing cancer in the other breast in the following years. next. The risk of remaining breast cancer increases with time from the diagnosis of unilateral breast cancer, the risk level is 20-30% after 10 years and 40-50% after 20 years.
.
- Ovarian cancer: About 1.2% of women in general are at risk of ovarian cancer. Meanwhile, the group of women carrying mutated BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 genes has 39-44% and 11-17% respectively at risk of ovarian cancer at age 70-80.
.
Some people who inherit genetic mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes do not develop breast or ovarian cancer, the reasons are:
+ In most cases, harmful variants are inherited from both parents, and the embryo will not develop.
+ If they inherit a harmful variant from one parent, they also inherit a normal copy of that gene from that parent. Cancer only occurs when a second mutation affects the normal copy of the gene. At that time, both copies of the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes do not function normally, leading to the risk of cancer.
.
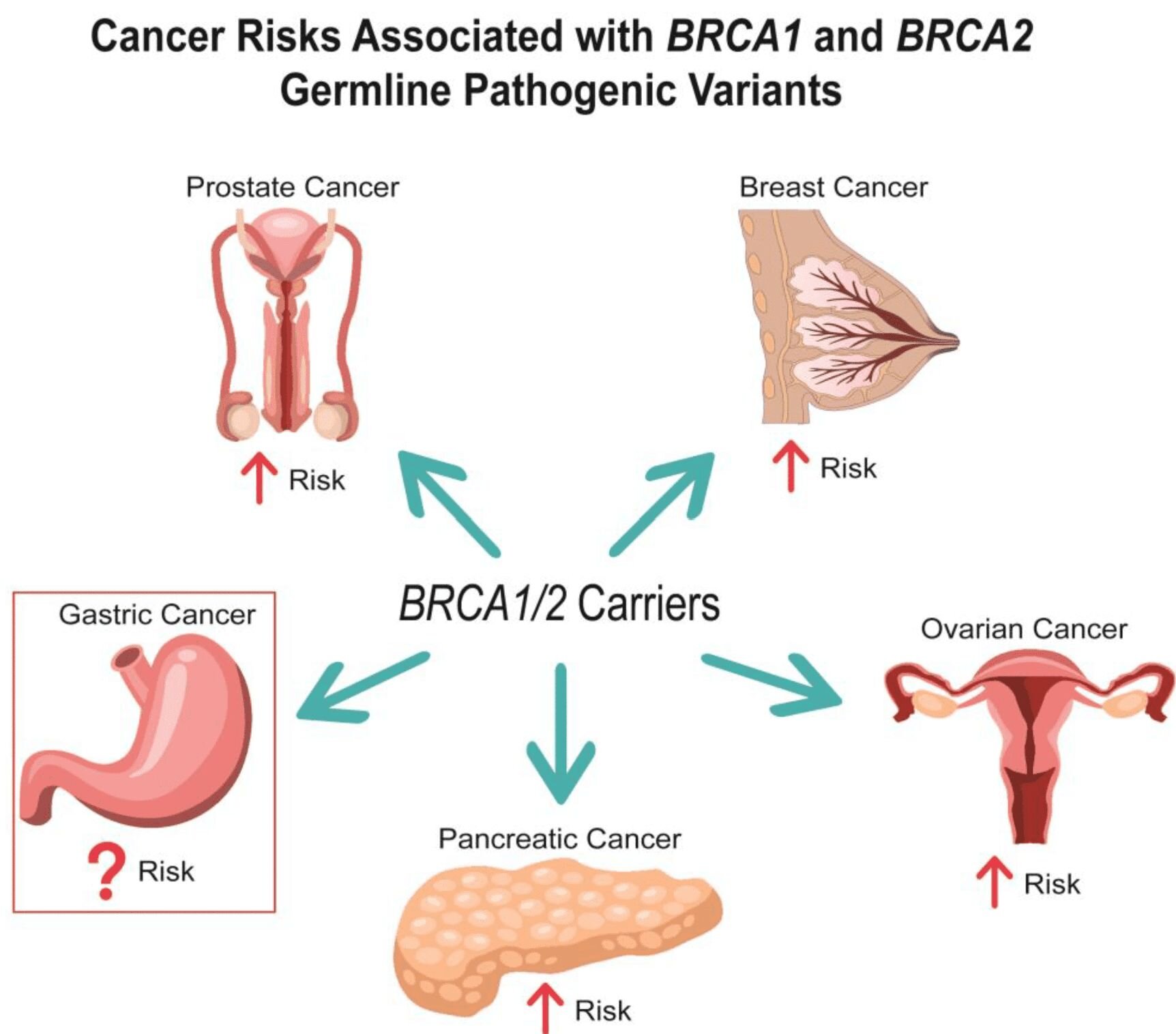
BRCA1 AND BRCA2 GENE MUTATIONS AND OTHER RELATED CANCERS
Mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes increase the risk of certain other cancers:
- Women carrying BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations have an increased risk of fallopian tube cancer and primary peritoneal cancer.
- Men carrying BRCA 1,2 mutations, especially BRCA 2, are at risk of breast cancer and prostate cancer.
- Both men and women carrying BRCA1,2 gene mutations have a higher risk of pancreatic cancer, although the increase in risk compared to individuals without the mutation is small.
.
In addition, some mutations in the BRCA1 and 2 genes can cause Fanconi anemia syndrome - a rare disorder of renal tubular function that causes impaired kidney function, causing excess substances. such as glucose, amino acids, phosphate, uric acid, potassium... are excreted in urine. The disease slows the body's development and damages bones and kidneys, endangering the patient's health.
.
Source of article:
https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/genetics/brca-fact-sheet
https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/disease/breast_ovarian_cancer/genes_hboc.htm





