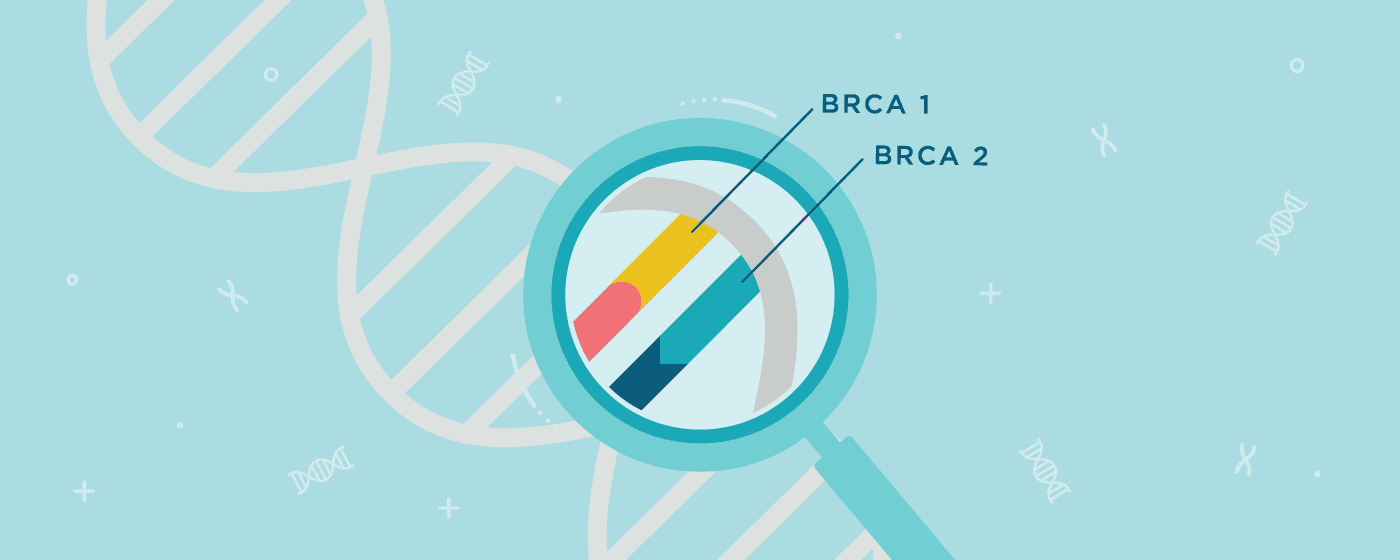
BRCA 1 & 2 Testings
What is BRCA1 & BRCA2?
Everyone is born with two copies of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, one from their mother and one from their father. Normally, the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are responsible for repairing damaged DNA.
.
What are BRCA1 & BRCA2 gene mutations?
BRCA1, BRCA2 gene mutations are when the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are mutated, preventing them from functioning properly. At this point, people with BRCA1, BRCA2 mutations face a higher risk of developing breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and other cancers. However, science has proven that not everyone with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations will develop breast cancer or ovarian cancer.
Groups with high risk of Cancer with Mutated Genes
When it comes to breast cancer risk, the most important inherited gene mutations are the BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations. Women or men with these gene mutations are said to have hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome.
Women with BRCA gene mutations have a higher risk of breast cancer, as well as an increased risk of ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, and possibly some other cancers. Men with BRCA gene mutations have a higher risk of breast cancer (although the risk is lower in women), prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, and possibly some other cancers.
If you have a family history of breast cancer, you are at higher risk of developing breast cancer. However, the gene mutation is more common in women with a family history of breast cancer, especially if the family history also includes other cancers, such as ovarian, pancreatic, or prostate cancer. The risk of having a genetic syndrome is also affected by:
- Which family members are affected (Cancer in a close relative, such as a mother or sister, is more worrisome than cancer in a more distant relative.)
- The number of family members affected
- The age at which your relative was diagnosed (Cancer occurring at a younger age is more worrisome.)
- Some other gene mutations
Inherited mutations in several other genes can also increase the risk of breast cancer, including the following:
- PALB2
- CHEK2
- ATM
- CDH1 (associated with hereditary gastric cancer)
- PTEN (associated with Cowden syndrome)
- TP53 (associated with Li-Fraumeni syndrome)
Therefore, screening and early detection of breast cancer is significantly important.
.
What makes BRCA 1, 2 testing important?
BRCA gene mutation testing is a blood test that analyzes DNA to identify harmful mutations in one of two breast cancer susceptibility genes, BRCA1 and BRCA2. To test for these mutations, a doctor takes a sample of a person's blood and analyzes it. This genetic test identifies any mutations in one of the BRCA genes. [2]
This test is used for people who are at risk for a genetic mutation based on a personal or family history of breast cancer or ovarian cancer. BRCA gene testing is not routinely performed on people at average risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
.
Why do you need to do BRCA 1, 2 test?
BRCA gene mutation testing helps to better understand a person's cancer risk. It also provides information to the patient's family about the genetic health effects.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations significantly increase the risk of breast cancer. People with BRCA gene mutations are six times more likely to develop breast cancer by age 80 than the general population. Cancer can still develop at an earlier age and is more likely to affect both breasts.
BRCA mutations can also increase the risk of:
- Ovarian cancer and two related cancers: fallopian tube cancer and peritoneal (belly lining) cancer.
- Prostate cancer.
- Pancreatic cancer.
- Fanconi anemia (a rare cancer that usually develops in childhood).
.
When do you need to do BRCA 1, 2 test?
If you are concerned about your risk because of a personal or family history of breast cancer, talk to your doctor. As a first step, your doctor may use one of several risk assessment tools. These tools use your family history and other factors to help you and your doctor better understand your risk of inheriting a BRCA gene mutation. But these assessment tools are not uniform, and each can give different results. Your doctor will discuss your risk and recommend appropriate genetic testing.
Includes two main groups of people:
- Women diagnosed with breast cancer: not all women with breast cancer need genetic counseling and testing. However, counseling and testing are more likely to be helpful if:
- You were diagnosed with breast cancer at a young age
- You have triple-negative breast cancer
- You have been diagnosed with a second breast cancer (not a first recurrence)
- You are of Ashkenazi Jewish descent
- You have a family history of breast cancer (especially at a younger age or in men), ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, or prostate cancer - Family history: people with a known family history of a BRCA gene mutation (or other genetic mutations)
Genetic counseling and testing may also be recommended for people at high risk for inherited gene mutations, including:
- Women diagnosed with ovarian or pancreatic cancer or men diagnosed with breast, pancreatic, or prostate cancer or metastases.
- People with a family history of breast cancer at a young age, multiple family members with breast cancer, or a male family member with breast cancer.
- People with a family history of ovarian, pancreatic, or metastatic prostate cancer.
.
Take notes when you do BRCA 1, 2 test
A test that looks for a small number of BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations has been approved by the FDA. However, there are more than 1,000 known BRCA mutations. This means that there are many BRCA mutations that will not be detected by this test. People who test negative may think they do not need to worry about their risk, when in fact they may still have another BRCA mutation.
.
Meaning of BRCA 1, 2 mutation test results
1. Positive BRCA gene mutation test
A positive BRCA gene mutation test means that you have a significantly increased risk of cancer. However, this does not mean that you will get cancer. Knowing that you have a BRCA gene mutation can help you take the initiative to get cancer screening tests. It also helps family members better understand their own risks. [4]
Consult your doctor about whether your loved ones can be tested. Your doctor can also explain the preventive measures you want to take. These steps may include:
- Regular cancer screening such as mammograms.
- Additional tests such as breast MRIs and breast ultrasounds.
- Limit the use of birth control pills, which can reduce the risk of ovarian cancer but increase the risk of breast cancer in some people.
- Prevent cancer with medication.
- Prophylactic mastectomy to remove healthy breast tissue before cancer can develop, and prophylactic oophorectomy to reduce the risk of developing ovarian cancer.
.
2. What a negative result means
A negative result for a BRCA 1 or 2 mutation test means that no gene mutation was found in your blood sample
A negative BRCA gene test does not guarantee that you will not develop cancer. You are still at risk for breast cancer like everyone else. Therefore, you should still have regular cancer screening
If the result is negative but one or more family members have had breast cancer before age 50, it is possible that the family has another gene mutation that increases the risk of cancer. Your doctor will advise you to better understand these results and decide if any further testing is needed.
In addition, there are factors other than genetics that increase the risk of cancer, such as childhood radiation exposure, and these factors should be considered when assessing cancer risk.
.
3. What does an inconclusive BRCA mutation test result mean?
Sometimes, the test gives an inconclusive result and requires further testing. The test shows a change in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes, but not a mutation associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
This BRCA mutation test result is a mutation of undetermined significance (VUS). Your doctor will explain these results and help decide whether you and your family should undergo further genetic testing.
If you have a BRCA gene mutation, your risk of developing breast cancer and ovarian cancer will increase significantly. Therefore, you should go to a reputable medical facility for advice and screening tests if necessary. Women can visit the Breast Surgery Department, Tam Anh General Hospital with experts, experienced doctors and many modern equipment from Europe and America to help test BRCA genes quickly, accurately and provide appropriate treatment.