According to statistics, each year in the world, about 7,500 women get breast cancer and 2,000 women get ovarian cancer due to genetic mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
As we know, BRCA1,2 gene mutations increase the risk of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and some other types of cancer. Additionally, people who inherit this mutation have an increased risk of developing breast cancer at a younger age than the group without the mutation. This mutation can be determined by genetic testing. In today's article, we will learn about the indications and meaning of genetic testing to determine BRCA1,2 gene mutations.
.
INDICATIONS FOR TESTING
The term predictive genetic testing refers to testing indicated for subjects with a family history of suspected BRCA1,2 mutations. BRCA1,2 gene mutations are relatively rare in healthy populations, so experts recommend testing only for at-risk cases. Cases at risk of carrying mutated BRCA1,2 genes include subjects whose family members have one of the following characteristics:
.
1.Breast cancer, especially breast cancer cases before age 50;
2. Ovarian, peritoneal or fallopian tube cancer.
3. Pancreatic Cancer.
4. Metastatic prostate cancer.
5. Ashkenazi or Eastern European Jewish race.
6. Known carriers of the BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation in the family.
.
MEANING OF GENETIC TESTING TO DETERMINE BRCA1, 2 GENE MUTATIONS
*Consulting process
When patients come in for predictive genetic testing, they will have one or two appointments to discuss issues related to the test, depending on their age and understanding of genetic information.
.
At your first appointment, your doctor or consultant will explain what a mutated gene is, how it is inherited, your risk of carrying the mutated gene, assess your risk of developing cancer, and your options. Cancer screening and preventive measures to reduce risks. The doctor will discuss with the patient when to conduct the test, the risks and benefits of genetic and psychological test results; daily life and family relationships.
.
If the patient decides to have a test, the doctor will conduct the test and arrange to return the results after one week (usually face-to-face instead of notifying by phone). Encourage patients to bring friends or relatives when coming to get results.
.
*Test results
After testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations, the results the patient receives may be positive, negative or an unclear result.
.
- Positive result
A positive test result shows that the person carries one of two mutated BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes. These genes are called “pathogenic” or “likely pathogenic” genes and are associated with a higher risk of developing certain cancers. However, a positive test result cannot confirm whether or not that gene will develop cancer or when. Some people who carry BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations do not develop cancer during their lifetime.
.
A positive test result is also very important in warning the risk of carrying mutated genes to family members and the next generation.
.
All people who are related to someone who carries the mutated BRCA12 gene will be at risk of carrying the mutated gene. For example, siblings of someone who carries a gene mutation also have a 50% risk of carrying the mutated gene.
.
It is very rare for an individual to test positive for a mutation in either of the BCRA1 or BCRA2 genes that is not inherited from a parent. If this occurs, it is called a de novo mutation, a mutation that occurs only in the eggs or sperm of the affected individual's parents. 'De novo' mutations can explain genetic defects that a child has when there is no family history of the disease. This mutation is present in all adult cells from that cell. Children of a person with a de novo mutation will be at risk of inheriting that mutation, but their siblings will not be at risk.
.
Some medical measures considered in people with BRCA1,2 gene mutations include: Advanced screening, risk-reducing surgery, and chemotherapy.
.
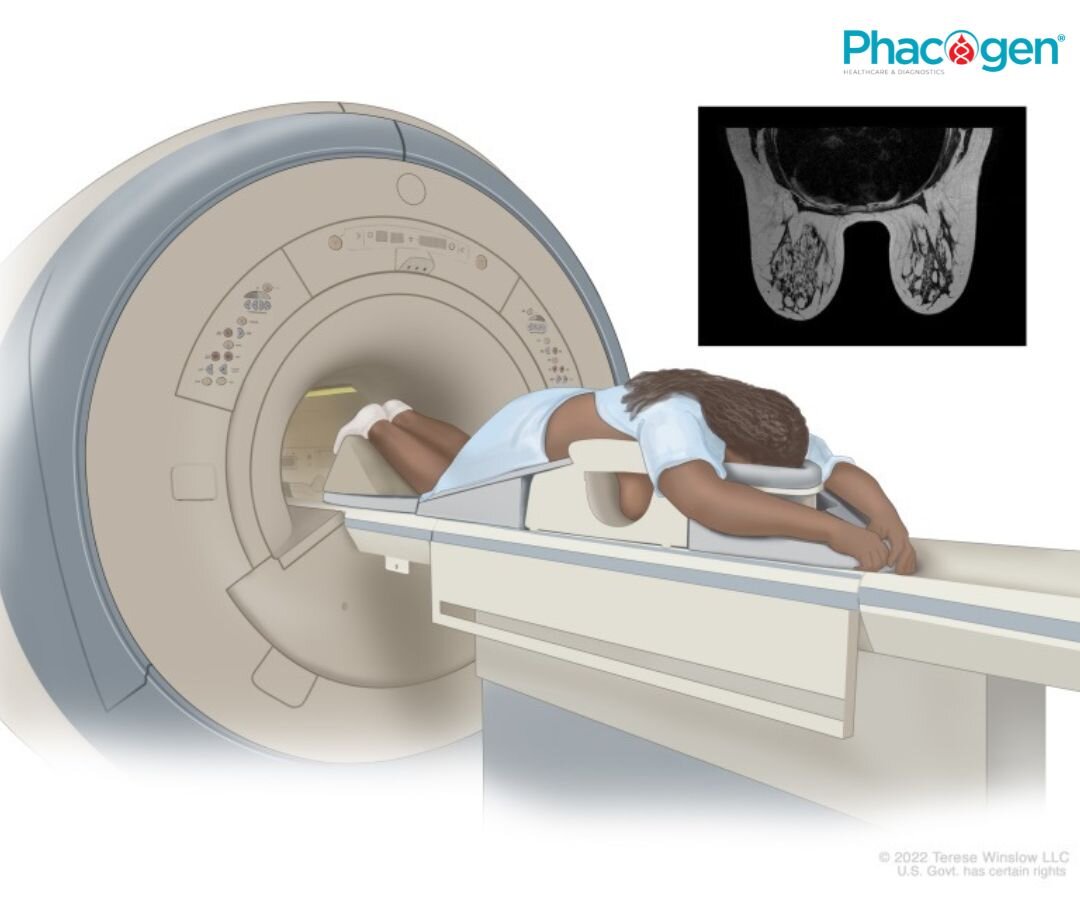
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) mammography is an imaging method used to screen for breast cancer in certain people at high risk of the disease.
.
- Negative result:
A negative test result has many meanings, depending on the individual and family history of the person tested. If the test result is negative while their relative carries the mutated BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene, it proves that the person being tested did not inherit the gene mutation from their family. A person with such a test result is called a true negative. Their risk of disease is similar to the general risk of disease in the healthy population.
.
If the person being tested has no history of cancer and their relatives are not known to carry the gene mutation, then in this case, a negative test result is considered “uninformative”. ”. There are a number of possible reasons why someone may have an incomplete negative test result.
.
- Vague or uncertain results: The test shows a change in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene but not a mutation associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. The result of this BRCA gene mutation test is a mutation of unknown significance. The doctor will interpret these results and help decide whether the person and their family should have further genetic testing.
.
The direct medical effects of genetic testing are minimal, but learning about a test result, whether positive or negative, can have negative effects on emotions, relationships, and relationships. Social, financial, etc. relationships of the individual doing the test and related people.
.
Reference:
1. A beginner's guide to BRCA1 and BRCA2, The royal marsden, NHS Foundation trust.
2. https://www.cdc.gov/genomics/disease/breast_ovarian_cancer/fam_hist_genes.htm





