On the afternoon of October 3, 2022, the Ministry of Health confirmed the first case of monkeypox in Vietnam. Previously, based on disease records from WHO, the Ministry of Health issued Decision No. 2099/QD-BYT on Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of monkeypox in humans.
- STAGES OF THE DISEASE
- CLINICAL PATTERNS
- BASIC TESTINGS
- Tests to diagnose the cause
- SUSPECTED DIAGNOSIS
- Suspected case
- Confirmed case
- Differential diagnosis
- TREATMENT
- Rules of treatment
- INVESTIGATION, CASE REPORTING AND TREATMENT ROUTE
- Investigate and report cases
- Treatment lines
- PREVENTION
- Non-specific prevention
According to WHO's updated report, from January 1, 2022 to July 22, 2022, the World Health Organization recorded 16,016 cases of monkeypox in 75 countries in all 6 regions. WHO, including 5 deaths.
.
Since 1970, monkeypox has been endemic in Africa (in 11 countries), with almost no cases reported in other regions. By May 2022, WHO announced the recording of cases in some European regions (the first cluster of cases recorded in the UK), this was the first time outbreaks were recorded in countries outside the African region. . Since then, the epidemic has continuously increased in both the number of cases and the number of countries, regions and territories reporting cases. Currently, a number of countries near Vietnam such as Thailand, Singapore, and Taiwan (China) have recorded imported cases.
.
During this epidemic, the main reported cases were men, homosexual men, and bisexual men (99% occurred in the UK, Spain, USA, Canada). In addition, an increase in the number of cases was also recorded in countries in the West and Central Africa region.
.
On July 23, 2022, the Director General of the World Health Organization announced that the current monkeypox outbreak meets the criteria for assessing an international public health emergency according to the Health Regulations. international; There is still much information about the disease that needs to be researched and learned more, especially about the mode of transmission of the virus.
.
On July 29, 2022, the Ministry of Health issued Decision No. 2099/QD-BYT on Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of monkeypox in humans, including the following main contents:
.
STAGES OF THE DISEASE
The disease progresses through the following stages:
- Incubation period: from 6 to 13 days, (ranges from 5 to 21 days). Infected people have no symptoms and are not infectious.
.
- Onset phase: from 1 to 5 days with main symptoms being fever and generalized peripheral lymphadenopathy. Accompanying symptoms, the patient may have headaches, fatigue, chills, sore throat, and muscle pain. The virus can be transmitted to others from this stage.
.
- Full-blown phase: characterized by the appearance of rashes on the skin, often occurring 1 to 3 days after fever, with the following properties:
+ Location: Phat An tends to be centrifugal, commonly found on the face, palms, and soles of the feet. The rash can also appear in the mouth, eyes, and genitals.
+ Rash progression: sequentially from macules (lesions with a flat base) to papules (hard, slightly raised lesions) -> vesicles (lesions filled with clear fluid) -> pustules (lesions filled with yellow fluid) -> dry scabs -> peeling and can leave scars.
+ Skin lesion size: average from 0.5 - 1cm.
+ The number of skin lesions per person can range from a few to dense. In severe cases, the lesions can join together to form large patches of skin damage.
.
- Recovery phase: symptoms of monkeypox can last from 2 to 4 weeks and then go away on their own. The patient no longer has clinical symptoms, scars on the skin can affect aesthetics and is no longer at risk of infection to others.
.
CLINICAL PATTERNS
- Asymptomatic form: people infected with monkeypox virus do not have any clinical symptoms.
.
- Mild form: symptoms usually go away after 2 to 4 weeks without needing any specific treatment.
.
- Severe form: often occurs in high-risk groups (pregnant women, the elderly, children, people with underlying diseases, immunodeficiency, etc.), can lead to death, usually within weeks 2nd disease.
+ Skin infection: the patient has a prolonged fever, the blister fluid is cloudy or the blister is broken and leaking cloudy fluid.
+ Pneumonia: the patient has symptoms such as cough, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing.
+ Encephalitis: impaired consciousness, seizures, confusion, coma.
+ Sepsis: prolonged fever, damage to internal organs.
.
BASIC TESTINGS
Non-specific changes in hematology and blood chemistry tests:
- The number of white blood cells in the blood may be normal or slightly increased; The number of lymphocytes is often reduced.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein (CRP), Procalcitonin (PCT) are normal or slightly increased.
- In some cases, there may be a slight increase in ALT, AST, and CK.
- In severe cases with signs of organ failure, electrolyte disorders and acid-base, do the following tests at units that can do it:
+ Blood culture, burn fluid culture to find bacterial causes in cases of suspected complications of skin infection, sepsis...
+ Chest X-ray or chest computed tomography in case of complications of pneumonia, lung abscess...
+ Brain CT scan or brain MRI in case of suspected encephalitis complications...
.
Tests to diagnose the cause
Molecular biology testing (PCR or equivalent) with pharyngeal fluid specimens (onset phase) and blister fluid (full-blown phase) for suspected cases to determine the cause according to regulations of the Ministry of Health. Ministry of Health.
.
SUSPECTED DIAGNOSIS
Suspected case
- A case with one or more of the following epidemiological factors:
+ Within 21 days before symptom onset, exposure to a confirmed or probable case, through direct physical contact with the skin or skin injury (including sexual contact) ), or contact with contaminated items such as clothes, bedding, and personal belongings of the sick person;
+ Have a history of travel to countries where monkeypox is endemic within 21 days before symptom onset;
.
- Clinical signs suggestive of monkeypox.
.
Confirmed case
Those who had a positive molecular biology test result for monkeypox virus.
.
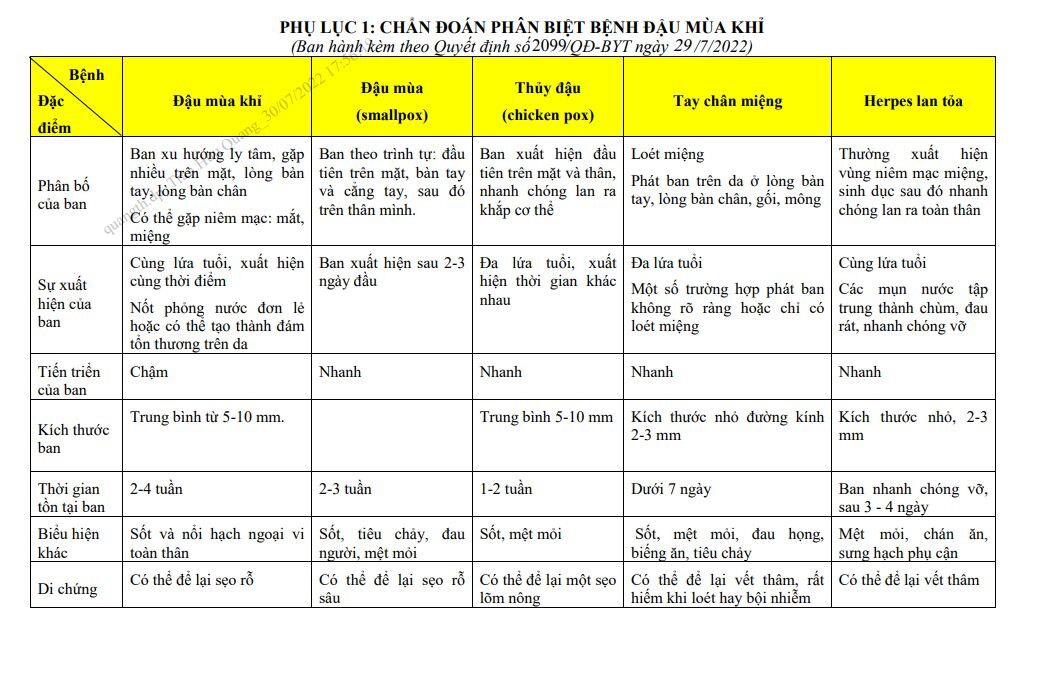
Differential diagnosis
Based on the symptoms of fever, rash and enlarged lymph nodes, it is necessary to differentiate monkeypox from the following diseases: smallpox, chicken pox, disseminated herpes, hand, foot and mouth disease.
.
TREATMENT
Rules of treatment
- Carry out surveillance and isolation of suspected/confirmed cases;
- Symptomatic treatment is mainly;
- Ensure nutrition, electrolyte balance and psychological support;
- Use specific treatment drugs in severe cases and special conditions (newborns, the elderly, immunocompromised people, etc.) according to recommendations of the World Health Organization and regulations of Vietnam.
- Monitor, detect and promptly treat serious conditions and complications of the disease.
.
INVESTIGATION, CASE REPORTING AND TREATMENT ROUTE
Investigate and report cases
Implement information and reports according to the provisions of the Law on Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases; Circular No. 54/2015/TT-BYT dated December 28, 2015 of the Ministry of Health guiding the regime of declaration, information, and reporting of infectious diseases and other documents on information and reporting of epidemics. The confirmed case report is sent to the Department of Preventive Medicine, Ministry of Health within 24 hours of receiving test results confirming the case of monkeypox virus infection.
.
Treatment lines
- At commune/ward, district/district health care: asymptomatic cases, mild cases with common symptoms of the disease.
- Provincial and central levels: severe cases or at risk of worsening (newborns, immunocompromised people, the elderly, underlying medical conditions, pregnant women); The case has serious complications.
- Dangerous signs of the disease need to be monitored and considered for referral for treatment:
+ Reduced vision.
+ Reduced consciousness, coma, convulsions.
+ Respiratory failure.
+ Bleeding, decreased urine output.
+ Signs of sepsis and septic shock.
.
PREVENTION
Non-specific prevention
General precautions to avoid monkeypox infection include:
- Avoid contact with people/animals who may be sick (including sick or dead animals in areas where monkeypox occurs).
- Avoid contact with objects and surfaces that are at risk of being infected with monkeypox virus, such as bed sheets and clothes of sick people.
- Isolation and treatment of patients at medical facilities.
- Regularly wash your hands with soap and common antiseptic solutions after contact with people/animals suspected of being infected.
- Use personal protective equipment when caring for patients.
- Conduct an exposure risk assessment according to regulations to take appropriate treatment measures.
.
Specific disease prevention with vaccines: Use vaccines to prevent monkeypox for high-risk groups.
.
Infection prevention at treatment facilities: Strictly implement isolation of suspected, possible and confirmed disease cases. Comply with infection control and infection prevention measures for medical staff and people taking care of patients.





